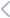You stroll into your favorite store, and it’s like they’ve read your mind. The perfect pair of shoes, the ideal shade of lipstick, and that gadget you’ve been secretly coveting — all right there, waiting for you. Ever wondered how they do it?
It’s time to peel back the curtain and discover the technology behind it all — big data!
What Is Big Data?
Big data isn’t just data. It’s about collecting a mind-boggling amount of information and turning it into a mechanism. It makes retailers know what you want before you even do it.
Big Data’s Five V’s
We usually break down big data with the five V’s that perfectly illustrate the core ideas behind its collection and use:
Volume: Every time you click, tap, or swipe online, it’s recorded. Retailers use these volumes of data to decode trends and crack shopping behavior.
Variety: Retailers scoop up data from everywhere — your purchases, social media posts, online reviews, and even the weather forecast.
Velocity: Big data isn’t a history book; it’s more like a live broadcast. Retailers change prices, restock shelves, and tailor ads in real time. Amazon is legendary for this — it adjusts prices every 10 minutes to stay ahead of the game.
Veracity: Data accuracy is the name of the game. Imagine if your online order said “in stock” but really wasn’t. Stores like Macy’s invest in tools to keep their data rock-solid.
Value: It’s all about the bottom line. Big data lets retailers craft personalized experiences and super-targeted ads to generate bigger profits.
The convergence of big data and the retail industry is a long story, covering the use cases, success metrics, innovations, examples, and more. Let’s first explore the most common applications and see what employees don’t have to analyze and adjust manually anymore.
Why and How Big Data and Retail Converge
The idea behind using big data in the retail industry is pictured by how small data points have a significant impact on shopper or retailer decisions. Some of the most common applications include personalizing shopping experiences, managing inventory, building pricing strategies, and detecting fraud — all with data.
Personalization

You know that feeling when Amazon suggests the perfect book you didn’t even know you wanted? Here, big data crunches your past purchases, browsing history, and even what others like you are buying to adjust recommendations just for you. All with the help of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Sometimes you may also receive an email with discounts for products you’ve been eyeing. Big data is behind that, too. It helps retailers send personalized promotions, increasing the chances that you’ll find something you love.
Inventory Management
Retailers no longer rely on gut feelings to stock their shelves. Big data analyzes historical sales data, market trends, and even external factors like weather to predict what customers want, ensuring products are available when needed. Walmart, for instance, uses big data to predict product demand with a 95% accuracy rate.
Another thing is stock optimization. It’s a delicate balance between having enough in stock without overloading your warehouse. Big data fine-tunes inventory levels, saving retailers money while making sure you can still grab that must-have item.
The mobile solutions for warehouse management make the picture even brighter. Workers can record inventory data on the go with no need to return to stationary kiosks. This amps up, cutting down on errors and costs, and ultimately improving productivity.
Read more about how Worker Activity Logs Give Valuable Insights in Inventory Management
Pricing Strategies

A good example is how retail flight prices change with big data depending on when you book. Big data analytics enables dynamic pricing, where product prices adjust in real time based on demand, competition, and even your browsing history.
Consequently, retailers keep an eagle eye on competitors. It helps them spot opportunities to price competitively or offer better deals to win your business.
Fraud Detection

Big data is like a digital detective, monitoring transactions for unusual patterns. If it detects something fishy — like an unusually large purchase or a transaction from a different country — it can flag it for further review.
Retailers can use big data to build models that predict which transactions are most likely to result in chargebacks. This proactive approach saves them money and helps keep prices lower for you.
Now that we’ve covered applications, let’s get technical. We’ll discuss where big data comes from, the numbers it produces, the cool innovations, and the tech that makes it happen.
And prior to this, we need to distinguish retail from e-commerce, which are very similar things but do differ in one main aspect.
E-Commerce vs. Traditional Retail
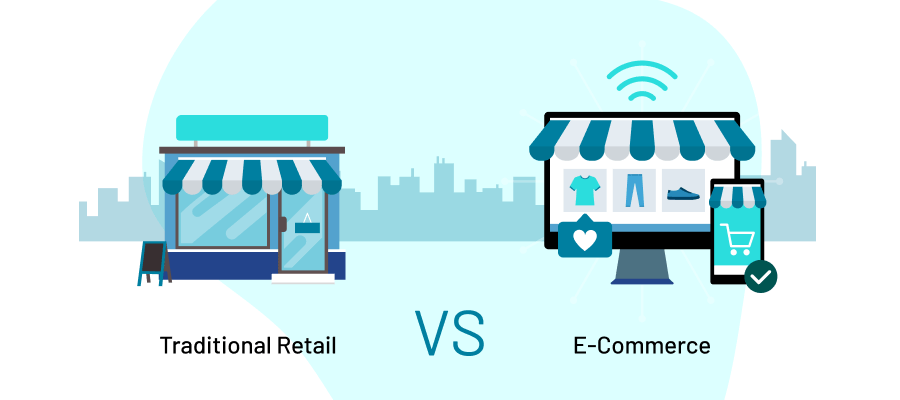
Simply, traditional retail happens offline, and e-commerce happens digitally. E-commerce is retail, but offline retail is not e-commerce.
In the e-commerce corner, we have a virtual shopping universe, where the stores never close, and your favorite products are just a click away. It’s a realm of digital transactions, algorithms, and personalized recommendations that shape your shopping journey.
Traditional retail, on the other hand, thrives in the physical world, where storefronts beckon you with tangible products to touch, try on, and take home. It’s about store layouts, foot traffic, and the art of engaging with customers face-to-face.
Some retailers operate in both worlds. Thus, if you are a case, consider the differences in success metrics tracked with big data for retail and e-commerce.
Success Metrics of Big Data in E-Commerce & Retail
To appreciate the synergy of big data and retail, let’s truly recognize the unique metrics that both offline retail and e-commerce utilize. In reality, tracking these metrics and sticking to their best values lets retailers build successful strategies regarding inventory management, pricing, and other areas mentioned before.
E-Commerce Metrics
Metric |
Type |
Description |
How to Calculate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primarily read-only | Read and write abilities | Read, write, and execute abilities | Read, write, and execute abilities |
| Conversion Rate | Behavioral | Measures the percentage of website visitors who make a purchase. | (Number of conversions / Total website visitors) * 100% |
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Financial | Evaluates the cost associated with acquiring a new customer./td> | Total cost of acquisition efforts (marketing, advertising, etc.) / Number of new customers acquired |
| Average Order Value (AOV) | Financial | Determines the average amount spent by a customer in a single transaction. | Total revenue / Number of orders |
| Cart Abandonment Rate | Behavioral | Tracks the percentage of users who add items to their cart but do not complete the purchase. | (Number of abandoned carts / Number of initiated checkouts) * 100% |
| Customer Retention Rate | Behavioral | Measures the percentage of customers who return to make additional purchases. | ((Number of customers at the end of a period – Number of new customers acquired during that period) / Number of customers at the start of the period) * 100% |
Traditional Retail Metrics
Metric |
Type |
Description |
How to Calculate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foot Traffic | Operational | Tracks the number of people who enter a physical retail store. | People Counting System / Time Period |
| Same-Store Sales Growth | Financial | Measures the revenue growth of established stores over a specified period, excluding new store openings. | (Current Period Sales – Previous Period Sales) / Previous Period Sales * 100% |
| Customer Dwell Time | Behavioral | Calculates the average time customers spend inside a store. | (Total time spent by all customers / Number of customers) |
| Store Conversion Rate | Behavioral | Examines the percentage of in-store visitors who make a purchase. | (Number of purchases / Number of store visitors) * 100% |
The data composing these metrics comes from a variety of specific sources, such as web analytics tools, sales records, POS systems, financial statements, and more. The ability to combine diverse data sources and track metrics effectively has brought many leaders to really innovative solutions.
How Big Data Analytics in Retail Market Drives Innovation

Alright, let’s get cozy with a quick and captivating story.
Imagine you’re in the heart of Silicon Valley, where technology innovation blooms like wildflowers in spring. Here, startups are reimagining retail using big data.
DreamAgility is rewriting the playbook on product data. Using Visual AI, they swiftly generate precise, multilingual product data from images, saving time and money that would otherwise be spent on manual data entry. Retailers are experiencing triple-digit sales growth, all while keeping costs in check, a rare feat in today’s competitive market.
Then there’s Obsess, an experiential e-commerce platform. They’re turning websites into immersive 3D virtual stores. It’s like stepping into a real shop, all from the comfort of your screen.
But here’s the mind-bender Spark Neuro. They’re decoding your brainwaves to understand your response to content. It’s not science fiction; it’s science-meets-commerce. They measure your attention span and emotional reactions, giving retailers unprecedented insights into what keeps you engaged.
These startups are creating more engaging shopping experiences, saving time and money, and even diving into the depths of our brains to understand what truly captivates us.
But what is the tech behind all this?
Big Data Tools for Retail
Let’s take a quick look at how retailer tools handle, store, and make the most of the data, with a nod to some key technologies in the mix:
Data Warehousing: Retailers turn to data warehousing solutions like Amazon Redshift and Snowflake. These platforms are like digital vaults, expertly organizing vast amounts of data, both structured and unstructured, with impressive efficiency.
Data Analytics Platforms: Tools such as Tableau and Power BI are the retail detectives, extracting precious insights from heaps of data. They’re the secret behind informed decision-making, helping retailers stay ahead of the curve and startups borrow the best practices and templates.
Machine Learning and AI: Retailers use machine learning and AI to forecast consumer behavior, fine-tune pricing strategies, and create personalized shopping experiences. It’s like having a crystal ball for retail.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Think of CRM software like Salesforce and Creatio as the retail memory banks. They manage and organize customer data, enabling retailers to tailor their marketing efforts for maximum impact.
Inventory Management Systems: Systems like SAP Integrated Business Planning and Oracle Retail are the backstage heroes. They provide real-time inventory data, ensuring that products are always in the right place at the right time, simplifying stock management.
Web Scraping: This is where the secret police come into play. Technologies like web scraping let retailers gather data from external sources, such as competitor prices and customer reviews without huge manual effort.
We hope this gives a rough overview of big data tools and techniques that deliver exceptional customer experiences and propel business growth in today’s retail.
Learn more about Retail Data Analytics Techniques, Software, and Advantages
Case Studies: Netflix, Tesco, Walmart
While it’s true that well-known industry giants like Netflix, Tesco, and Walmart often dominate the spotlight in retail and e-commerce success stories, it’s essential to remember that the power of big data extends to SMBs as well.
Any retail business, regardless of its size, can produce successful use cases of big data by implementing a solid data strategy in its workflow.
Netflix: Personalized Content Pioneer
Netflix, although not your typical online store, has completely changed the way we enjoy entertainment. At its heart is a data-powered approach that customizes the viewing experience for millions of subscribers worldwide.
Netflix employs advanced algorithms that dig into your watch history, your likes and dislikes, and even the selections of folks who share your taste. This data forms the bedrock of its uncanny ability to suggest movies and TV shows tailor-made just for you. It’s not just about what’s trending; it’s about what’s perfect for you in the moment.
This high level of personalization keeps viewers hooked and happy, ultimately driving Netflix’s impressive growth and customer loyalty.
Tesco: Reducing Food Waste with Supply Chain Optimization
Tesco, one of the world’s retail giants, showcases the tremendous influence of data analytics in supply chain management. To cut down on food waste and streamline its supply chain, Tesco places great emphasis on data analysis.
By tapping into sources such as point-of-sale systems and inventory tracking, Tesco obtains up-to-the-minute information on product demand. This allows them to manage their inventory smartly, lowering the chances of perishable items getting wasted.
Through data-driven inventory choices, Tesco not only reduces its environmental impact but also delivers fresher products to customers, elevating their shopping experience.
Walmart: Data-Driven Inventory Management and In-Store Experience
Walmart, another retail giant with a vast physical presence, is a prime example of how big data can transform traditional supermarkets. Walmart uses data analytics extensively for inventory management and demand forecasting.
Through the analysis of historical sales data, weather forecasts, and even social media trends, Walmart ensures that its stores are well-stocked with the right products at the right time. This approach minimizes stockouts and overstocking, saving costs and enhancing the customer experience.
But their journey doesn’t stop there. Walmart also utilizes data to optimize its in-store experience. For instance, it uses the Check Out With Me program, which equips employees with mobile apps to provide speedy checkout assistance to customers anywhere in the store.
Whether it’s personalizing content at Netflix, reducing food waste at Tesco, or optimizing inventory management and in-store experiences at Walmart, big-data retail examples are shaping the future of these businesses and their interactions with customers.
Now, let’s dive into the less exciting but important subjects of security, ethics, and risks tied to using big data in retail. It’s like the “vegetables” of our retail data discussion — not the most fun, but necessary!
Ethics and Risks of Big Data in E-Commerce
In fact, these issues matter in any data-driven initiative. We just once again remind you that having all perks comes with great responsibility and potential hurdles.
Data Privacy and Security

In the era of big data, safeguarding customers’ personal information defines the brand’s reputation and user real safety. E-commerce and retail companies must navigate the ethical concerns surrounding data privacy and security, ensuring that sensitive data is protected from breaches and misuse.
As we checked out those innovative startups earlier, you might’ve noticed they’re diving into some pretty private space, like analyzing brainwaves. The rules and regs on such things are usually lagging behind. Technology zooms ahead, and the rule-makers are still catching up. So, it’s a bit of a Wild West when it comes to ethics and privacy.
Data Integration
As retailers collect vast amounts of data from various sources, the challenge lies in integrating this data effectively. Ensuring that data is accurate, consistent, and accessible across different systems is essential for informed decision-making.
Scalability

The scalability of online retail platforms to handle increasing data volumes is crucial. Rapid growth can strain existing infrastructure, affecting website performance and customer experiences. Ethical concerns arise when businesses struggle to meet demand due to scalability limitations.
Skill Gap

The field of big data requires specialized skills. Retailers may face challenges in finding and retaining talent with the necessary expertise in data analytics, machine learning, and data security, creating an ethical responsibility to invest in skill development.
Lack of Developers
Find out how to deal with the lack of IT talents without compromising project delivery.
Still, securing big data and keeping it ethical is worthwhile as its importance continues to grow.
Now, as we move on from the not-so-fun stuff, let’s wrap up with a final word on the promising future of big data analytics in retail. It’s all about staying confident and innovative as we step into this exciting landscape!
Trends in Big Data and Retail
Imagine the shopping life in the upcoming years. You enter the world of IoT and e-commerce. Your smart fridge might reorder groceries for you, and your wearable might suggest new workout gear when it senses you’ve been hitting the gym regularly. IoT is all about making tech feel more human, bridging that gap between the digital and the personal.
Now, let’s talk trust. With all these online transactions, blockchain changes the way they happen. It adds layers of security and transparency, making you feel even safer when you click that Buy Now button.
Have you ever considered shopping in a virtual store? Well, that’s where v-commerce comes into play. It’s like stepping into a digital mall where you can interact with products before you buy them.
And speaking of interacting, imagine trying on clothes virtually with AR/VR. You can see how that shirt looks on you without ever leaving your room. It’s changing the way we shop for fashion.
When it comes to supply chains, predictive analytics is making waves. Retailers are using data to predict what and when you’ll want to buy next, ensuring products are in stock when you need them.
But it’s not just about convenience; it’s about going green too. Green e-commerce is all about sustainable practices, from eco-friendly packaging to reducing emissions in delivery.
And let’s not forget about crypto. Some forward-thinking retailers are even accepting cryptocurrencies as payment, opening up a whole new world of possibilities.
There you go — a glimpse of the trends that will shape the retail and e-commerce setup with big data in the coming years. Globally, it’s a real transformation of our ordinary routines and personal lifestyles.
Conclusion
So, we’ve explored the incredible analytics potential, innovations, and ethical considerations that come with big data in retail. From personalized shopping experiences to supply chain optimization, it’s clear that big data is reshaping how we shop and do business.
Stay tuned for more fascinating insights, and if you’re hungry to integrate big data in your retail project, don’t forget to drop us a line, so you get an extensive consultation on how big data fits you. See you in the next chapter!