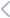What is a tech stack? What is its significance to a software solution? And what should a not tech-savvy project owner know about the technologies used?
This article sheds light on various technology stack types and modern tools, what they are used for, and the factors that dictate the best choice.
What Is a Technology Stack?
A tech stack in IT projects is similar to building materials in a house. It is the list of programming languages, tools, and frameworks that software developers combine for the creation of web and mobile applications.
The term “Tech Stack” is used because when developing an application, several layers are built over each other. The layers involve the use of different programming codes, components, and hardware modules, hence forming a stack of various technologies.
Structure of a Tech Stack
Now, that we’ve covered what is a technology stack, let’s examine its primary categories commonly employed in software development. The structure of a tech stack consists of two basic parts called the client-side and server-side, also referred to as frontend and backend.

The Frontend Tech Stack
The frontend is the user’s side; this is the interface that enables the user to interact with the program. Its primary purpose is the provision of access, convenience, a pleasing user experience, call to actions, and events.
There is a lengthy list of technology stacks that can be employed for both mobile and web frontend development. In general, they all relate to the combinational use of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and other technologies directly or indirectly. Hence, we will focus only on the main ones.
For Web
HyperText Markup Language (HTML) is used for building and placing content. All the positioning and order of page contents are done by this language.
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is for the objectification and representation of content materials. Mostly it involves the application of fonts, colors, layout characteristics, background contents, and so on.
JavaScript is also a role player. Its popular use is as a scripting language in browsers to enable interactivity in web pages. Today, there are numerous JavaScript libraries like jQuery, Bootstrap, and Slick fitted into frameworks such as Angular, Vue.js, and React that allow adding powerful functionality to your user interface.
Learn more: 5 Steps to Create a Website
For Mobile
Mobile frontend technologies can be categorized as native and hybrid. Hybrid development is based on the use of cross-platform web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
In its turn, native development is based on the use of native or cross-platform programming languages. For example, Java and Kotlin go well for Android, whereas Objective-C and Swift — for iOS. And React Native, Xamarin, and Flutter can deliver both Android and iOS apps. The use of a native mobile app development approach is much more preferable today as it allows more control and easier hardware access.
Learn more: Mobile Technology Stacks for Native App Development
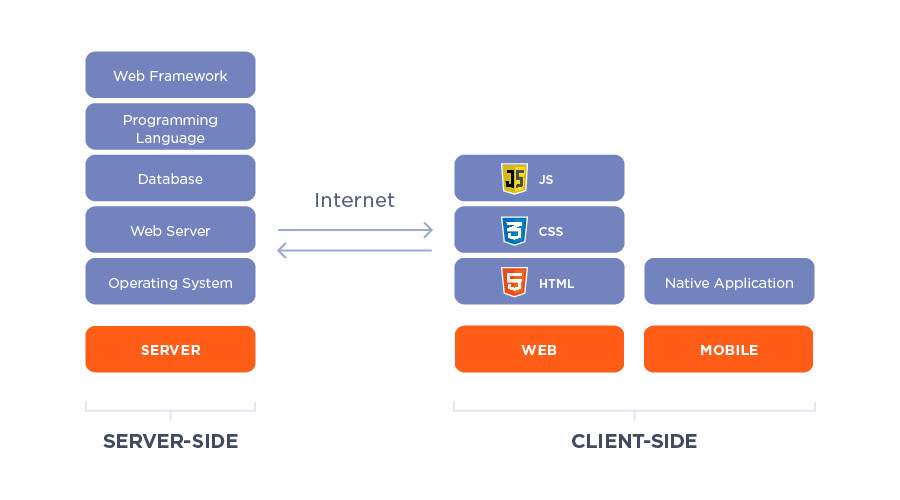
The Backend Tech Stack
The backend is comparable to the engine block that propels an application. It ensures the proper functioning of all the features responding to user requests such as access to the database and executing CRUD operations – Create, Read, Update, and Delete.
Backend constituents include programming languages, servers, server-side frameworks, OSs, databases, and APIs. In current backend development, these elements are supported by business logic, hosting, deployments, and cloud infrastructure. Modern backend technology stacks include MEAN, MERN, and LAMP. We’ll talk about them in detail further on.
While PHP remains a popular tech stack for legacy systems and content management platforms like WordPress, newer projects increasingly favor JavaScript and Python for backend work. Python frameworks like Django and Flask are preferred for fast development and prototyping, while Ruby on Rails, although reliable for it too, has seen a decline.
If you’re thinking about enterprise app development, then .NET, particularly .NET Core, continues to be a good choice. And if high performance is a focus for your web application, including Go and Rust in the technology stack will help you address the need.
In general, as businesses today require more scalability, backend architectures are shifting toward serverless models, containerization with Docker and Kubernetes, and microservices. Plus, CI/CD pipelines and cloud-based hosting have now become standard practices for deployments.
Middleware
Middleware is software that integrates two or more systems, applications or components for easy communication. Note that middleware is not a developer tool. It functions as a hidden translation layer that connects the backend and frontend parts of an application.
It is a recherché usually written in Java or C# to enable parsing, communication, and management of data between your app and server or database. The role it plays is vital in the distribution process of real-time actions, which is beyond sending requests and responses back and forth to the client and server.
Middleware consists of application servers, web servers, content management systems, and other related tools that support the development and delivery of applications.
Factors Affecting Tech Stack Selection

A tech stack is consequential because it’s what you use for creating software programs. Thus, don’t underestimate the essence of research and analysis to select the right set of tools.
A wrong choice of technologies can cause you the loss of money, time, and other valuable resources for your project. A sound business analyst and well-experienced developers are needed to avoid pitfalls when choosing your set of technologies.
Here’s the list of necessities to consider when picking a purposeful tech stack.
Defining the Platform
What are the expectations of the project? This is an important pointer. Without an understanding of what you expect from the project, choosing a software development stack is a futile move.
At this point, you should ask yourself who are my target audience. How they will use your app, when and where. What is the popular active device among them? Is it a mobile phone or a regular computer?
For instance, a web application requires a totally different set of tools and frameworks from a mobile app. Even within mobile applications, tech stacks you need for Android and iOS development are different.
You should then plan based on your answers and decide if you need a single or multi-platform solution to choose the best tech stack to use. Keep in mind that if you are making an MVP first, it is better to make it on a prominent platform popular among your target users to save software development costs and get user feedback promptly.
Learn more: How to Prioritize Features for Mobile App MVP
It doesn’t matter if it’s going to be a mobile or web application. MVP is vital to the success of your product and the development process. After defining the platform, consider all functional and non-functional parameters that are essential for the project launch. A set of well-defined requirements for MVP will finger the tools you need to reach your aim and the additional tech stack you may need for the market version.
Defining the Project Type
After you cross the bridge of defining the platform, you still have more analysis to make for choosing the right technology stack. You will be considering the project based on its size and complexity, processing strength, and business goals. For example, if your application involves multiprocessing or requires low latency for better responsiveness, then you must consider the relative tech stack that provides such support.
Small Projects
They are usually fast to deliver due to simple requirements and can be implemented with less sophisticated technologies like CMS or WordPress in the case of web projects.
Mid-Size Projects
For mid-size projects, there is a higher level of technological commitment. They may call for the use of several combinations of programming languages and tools depending on requirements and platforms. Such initiatives require technologies that provide more sophisticated and diverse functionalities and integrations.
Complex Projects
If you intend to create a social network, online marketplace, CRM, or order management system, then you are looking at a complex project. The combination of multiple programming languages is inevitable for such. This is just like the case of a mid-size project but with more complex features. You need several functions, integrations, and more sophistication, hence, your tech stack must be of a high level.
Scalability Requirements
The role of a tech stack in the scalability of an application is to make provision for the increase in users and functions. Your developers should make a choice of the technologies that will make room for new engaging features, user growth, and a seasonal rise in the number of users.
Your provision for scalability must cover horizontal scaling which involves several application servers running at the same time to handle the flow of user traffic, as well as vertical scaling for the inclusion of more programs to process new data types. Scaling horizontally and vertically will protect your application from crashing when the stormy days come.
Technology and Team Expertise
You need to weigh the expertise of your team and use it as a basis to judge your choice of the tech stack, except when you are looking to outsource. Developers usually have the command of some programming languages and tools more than others, so it all boils down to how skillful your team is.
You have to be certain your team can successfully follow through the use of a tech stack, or else, there is no need to use such a stack. To avoid employing an expert to cover up for the technology your team lacks, you can train them.
That is if you have the luxury of time. However, if you are pressed by deadlines just outsource the project. Therefore, it is paramount to match the skills and experience of your team and see that it matches the choice of technology. Platforms like DesignRush can be very handy for picking the right agency in this case.
Also, try to ensure your choice of tech has a big developer community and the availability of reference documents such as it is on Github and Stackoverflow. This would help your team not to get stranded on a tool or technology.
Lack of Developers
Find out how to deal with the lack of IT talents without compromising project delivery.
Maintenance
You need to consider that your team must be able to maintain the application after it is released. This is the next lane after you have developed your app, and it is related to your choice of tech stack, too.
Codebase
Your choice of tech stack should be motivated by software architecture and existing codebase if you want feasible maintenance. Try choosing languages that are effective with short, reusable, and easy-to-maintain codes. Your codebase should be simple and of average length. It helps developers to spend a short interval of time in trying to review, debug, and process the codes.
Software Architecture
Software architecture is a key player for enabling scalability, portability, and reusability of applications. Your choice of tech stack should be guided by your software architecture.
Based on this, you should consider technologies that enable both static and dynamic component configurations. It makes the performance of the application seamless, even when users increase or you add more engaging features.
Learn more about Microservices vs. Web Services Architecture
The Cost Implication of Tech Stack
Money makes the world go round they say. Besides, nothing comes for free. It’s no surprise that when it’s time to choose a technology stack for your software project, financial considerations play a significant role. However, it’s worth noting that there exists a multitude of popular open-source IT frameworks and tools that are free.
However, they come with subscription fees if you will need some special or advanced features. You might need to pay for licensing, and there is also the cost of maintenance. The choice of tech stack can lean on all these factors.
Furthermore, some tech stacks demand high salaries for their developers, so you need to consider that too. You might also have to look at the cost of training developers for a particular tech if it is an option. The tug of war is between the overall cost of using a tech stack and the effectiveness of its features.
Some Popular Tech Stacks
.NET Stack

.NET framework is a core tech in Microsoft’s technology stack. The Common Language Infrastructure from C#, F#, VB.NET, Fantom, etc. has provided a variety of over 60 frameworks, platforms, SDKs, IDEs, SOA, and libraries just to mention a few.
If you desire a dynamic and interactive web app, then you should be eyeing .NET development. It is a widely used and trusted framework for such purposes.
Learn more: Velvetech named a Leader among the top .NET developers in Chicago
You can also use .NET alongside other open source technologies, to build different types of server-side web applications or processing systems for enterprise-level transactions. As a subset of the Overflow Stack family, it is well qualified as an all-inclusive tech stack for the development of web front-end and database.
The runtime for .NET applications is very fast, yet, it is easy to develop, enabling developers to meet the deadlines. Interoperability with various platforms makes room for a variety of features to be created. That’s what the top .NET developers take advantage of.
.NET applications can be ported easily, so developers can choose any framework or technology to work with. It also allows developers to work with other languages.
Lastly, the use of code access security (CAS) to protect its programs. The common language runtime (CLR) of the .NET framework can manage its code to deny access to execute operations with a limited set of permissions.
LAMP Stack

The LAMP stack is a popular open-source software set. It mainly consists of the PHP programming language, Linux operating system, the Apache HTTP Server, and the MySQL relational database management system.
LAMP is trusted and has been around for a long time. It also works with Perl and Python as substitutes for PHP. Developers use it because it is ideal for dynamic websites and applications. Its combination with other open-source programs gives it interoperability, usability, and customizability.
Other variants of LAMP include:
- LAPP (Linux/Apache/PostgreSQL/PHP): It possesses a PostgreSQL database variation that’s configured to function with enterprise-level projects.
- XAMPP (Linux, Mac OS X, Windows/Apache/MySQL/PHP, Perl): It is a more complete stack that runs on Linux, Windows, and Mac operating systems. It also has an FTP server, which is cross-platform.
- WAMP (Windows/Apache/MySQL/PHP): It is an alternative to the Microsoft Windows OS. It is comprehensive and easy to use.
- MAMP (Mac OS X/Apache/MySQL/PHP): It is an alternative to Mac OS X operating system useable by both Windows and Mac.
MEAN Stack

MEAN stack is another open-source software set used by JavaScript developers for making dynamic web apps and websites. Subsequently, it is a perfect choice for developing scalable apps.
The MEAN Stack is made up of:
- MongoDB – a NoSQL database;
- Express.js – a web app framework that runs on Node.js, and Angular.JS;
- Javascript MVC – a framework that runs in-browser JavaScript engines;
- Node.js – an execution domain for event-driven server-side and networking applications.
Due to support programs written in JavaScript, the MEAN stack enables easy development of applications for both client-side and server-side environments. This also helps developers working on the client side to understand the codes of the server side.
MEAN supports the MVC pattern, and it is mobile-friendly due to interoperability with AngularJS. Finally, it allows the data transfer by using NoSQL’s native JSON and gives access to the Node.js JavaScript module library.
Another variant of MEAN is MEEN: MongoDB, Express.js, Ember.js, and Node.js.
Corporations and Tech Stacks
Most big corporations can say part of their success depends on the choice of tech stack. Some of them have made progressive efforts compared to when they just started by changing or adding to the technology they use.
Note that each of the technologies mentioned could include a list of individual or sub tech stacks, such as libraries, hosting environments, utilities, and so on. The business functions of an application usually dictate the tools to be used for its development. For the record, here are the main technologies some popular companies use.
Airbnb Tech Stack

- Programming Languages: JavaScript, Ruby
- Framework: Rails
- Databases: MySQL, Amazon RDS, Hadoop
- Server: NGINX
Facebook Tech Stack

- Programming Languages: PHP, GraphQL, Hack
- Framework: Tornado
- Databases: Cassandra, RocksDB, Beringei, Memcached
- Server: custom/proprietary
Pinterest Tech Stack

- Programming Languages: Python, Java, Go
- Framework: Django, Javascript MVC
- Databases: MySQL, Hadoop, HBase, Memcached, Redis
- Server: NGINX
Uber Tech Stack

- Programming Languages: Python, Java, Go, Objective-C, Swift
- Framework: Node.js, Apache Thrift
- Databases: MySQL. PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Redis
- Server: NGINX
Deciding the Destiny of Your Project
So, how to choose a technology stack? As we’ve found out, it depends on the requirements and skills of the team that will develop it, even if money is not a challenge. This decision can make or break a project. You should research similar types of products to what you intend to develop to see how they were built.
You can further consult your BAs, PMs, and developers to decide which frameworks and tools work best for the intended project. You might want to hire new developers or train the old ones if your team is found-wanting.
Velvetech will be glad to provide you with consultations and assist you with your software initiatives. We will suggest to you the most appropriate tech stack and project management methodologies that guarantee successful delivery. Learn more about our software development services and contact us today.