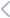If you are thinking about building a mobile app, then considering what platform to start with could be the first thing on your mind. What are the differences between iOS and Android app development? And how will the choice of the platform impact the success of your solution?
While your ultimate goal can involve launching the mobile app for two platforms, it might be risky and expensive to deliver iOS and Android apps at the same time. Before talking about the key factors that influence the choice of OS, let’s take a look at the market details that also help come to a decision.
Mobile OS Market Share
If your company’s strategy is to reach the global mobile market, then take into account the following numbers from StatCounter. Android remains the dominant operating system on the worldwide level holding a share of around 70% and leaving iOS with 30%.
Source: StatCounter Global Stats – OS Market Share
However, when it comes to the statistics by region, the situation looks a bit different. For example, you should probably deliver the iOS app first while aiming for the US market.
Here are the details for various world parts:
- North America: iOS – 54.3%; Android – 45.2%
- South America: iOS – 14.3%; Android – 85.3%
- Europe: iOS – 33.8%; Android – 65.6%
- Asia: iOS – 19.4%; Android – 89.9%
Bearing in mind the aforementioned, it makes sense to dive deeper into other differences between OS. Ultimately, making a choice can be narrowed down to 7 factors.
Choosing a Winning App Development Strategy
Watch our webinar to uncover effective mobile development approaches and launch your app.
Top 7 Differences Between iOS and Android Apps
1. Target Audience
In most scenarios, success comes to those who know their customers and how to meet their requirements. When setting goals for your business app, the target audience should be one of the top priority aspects to think about. Choose the platform according to the preferences of users whose needs you are trying to cover.
Of course, the users of iOS and Android are not as different as chalk and cheese, but still, there are variations in demographic breakdowns. As measured by Statista, 65% of US smartphone users in the 18-34 age group prefer iOS, while 35+ users tend to use Android.
Besides, most females consumers prefer Apple software, contrary to males who are inclined to use Android. As a general rule, iOS users have a higher annual income and spend more hours on the phone. Knowing this data can help companies target their future app more precisely and determine what operating system should be a starter.
2. Development Timeline

If the speed of development is crucial for your project, then it is good to know beforehand how much time it requires to deliver an iOS or Android solution. On average, it takes 30% to 40% longer to build an Android-based application in comparison with iOS. This is due to the code complexity and a wide range of devices.
On the contrary, the App Store has a stricter application review and acceptance process that lasts up to one week and involves a manual approach. Google Play adheres to automated tests that apps go through, taking a shorter period of time.
3. Development Budget
What platform to choose first to stay on budget?
Well, the total cost of mobile app development depends on many factors, including business requirements, feature set, and a team working on your app. In other words, it’s all about time to build an app. As we have mentioned above, developing an Android app needs more of this valuable resource, and usually, more time-consuming means more expensive.
Learn How Much It Costs to Make an App
Additionally, there is a fee for publishing an app on the marketplace that varies depending on the platform. Apple charges $99 yearly, whereas Google enables you to deliver your Android app for a one-time fee of $25.
Building an app with a limited budget is never an easy task. Having said that, there are several tricks to create a high-quality mobile app without going broke.
4. Monetization Strategy

There is a great number of app revenue models. However, you do not need to go through all of them to get the idea of which operating system would bring you the most. Basically, three main ways to get profit from mobile apps are:
- Paid applications
- In-app purchases
- Ad-based model
Both OS focus on different revenue sources according to various target audiences.
When it comes to paid products, iOS users are more prone to purchase the apps, while Android users tend to download them for free. That explains why the majority of Google-supported applications generate revenue from in-app ads.
Another way to monetize your mobile solution is to enable in-app purchases. This model works well for both OS, generating 48.2% of all mobile app earnings. However, there is a difference in the average purchase price per user for each OS. For Android, this is $0.47, and for iPhone owners – $1.
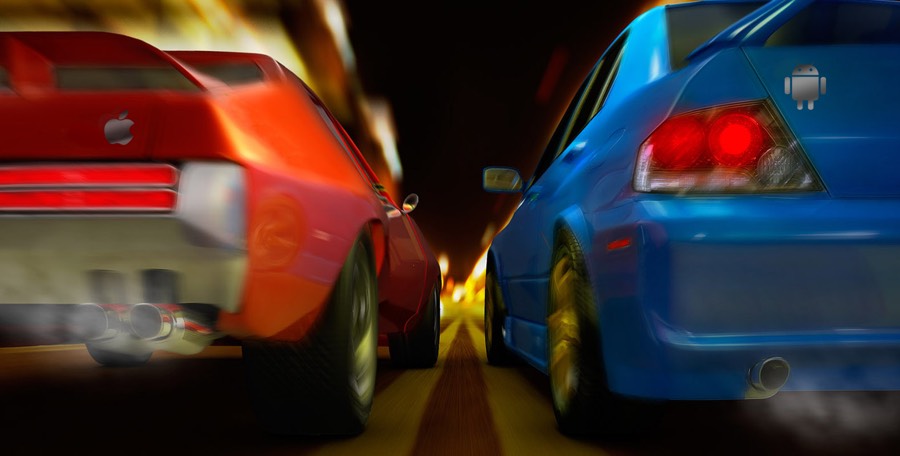
This is one of the reasons why the App Store has a higher income than Google Play according to the statistics of global customer spending.
Source: data.ai
Although recent data from Q3 2022 shows a modest decline in worldwide app consumer spend, there’s good news: in Q1 2023, both iOS and Google Play experienced growth, with iOS earning $21.7 billion and Google Play generating approximately $12.2 billion.
5. App Development Process
The complexity of the development process greatly depends on the set of features and the app’s functionality. Nevertheless, when it comes to building mobile apps for different operating systems, there are some nuances impacting the development and even testing phases.
Development Languages and IDEs
Some time ago, creating an Android app required more coding than iOS and, therefore, more time when developers used Java. Today, iOS and Android apps mostly operate with Swift and Kotlin languages. They both enable writing less code to complete the app and provide efficient performance.
In addition to different programming languages used for native app development, there are various IDEs suggested by Apple and Google. Previously, apps were majorly built with AppCode and Eclipse, while currently, developers apply the latest tools – Xcode for iOS and Android Studio for Android.
Development Approaches
If the speed of development, costs, and complexity play a vital role in your decision-making, then it is worth considering different mobile development approaches. Some of them will even allow you to deliver an app for both platforms at the same time.
Find out What Development Approach Will Benefit Your Vision the Most
You can opt for cross-platform development instead of two native applications. This approach can help you launch the product and reach a wider audience faster.
Read more about The Reasons to Build a Cross-Platform Mobile App
Of course, as nearly everything in our life has pros and cons, this approach also carries some moments to weigh. For instance, performance or customization is not the most powerful side of this approach.
Device Fragmentation
Another point drawing attention to comparison is device fragmentation. From this side, iOS development seems easier since Apple releases a limited range of devices.
On the contrary, Android apps should be compatible with dozens of devices with different screen sizes, hardware specifications, and versions of OS. That adds some complexity to the development process. It also extends the time for the QA phase as you need to test your mobile solution on a variety of devices to ensure its quality and smooth user experience.
6. Design and UX
Of course, as users of iOS and Android platforms, we all know how it feels to interact with them daily. And it is our user experience that makes us stick to one or another OS. The operating system dictates style and rules for app design and greatly impacts user engagement.
Read more about How to Drive Mobile App Engagement
The contrast between iOS and Android user interfaces is literally obvious. No wonder the design of the apps turns out to be different as well. Even if both platforms tend to follow simple visuals and a minimalistic approach, each provides a unique sense of flow.
The characteristics that differ include:
- Navigation bar
- Back button
- Menu
- Pop-up notifications
- Icon sizes
- Screen resolutions
- Control design
- Typography
The design strategy is one of the most distinctive moments to consider in iOS vs. Android app development. Following fewer variations of screen sizes, iOS apps are more predictable in terms of look. In contrast, many screen sizes and resolutions of Android devices increase the time to adapt and customize layouts, thus making it harder to cater to all the needs invariably.
7. Distribution and App Store Optimization
After the development process is over, your application is ready to see the world. At this moment, app stores take on the role. In the previous sections, we have covered some differences between the App Store and Google Play, like approval of the app and fees for publishing. Now let’s pay attention to some other important points.
The variety of apps in both marketplaces is constantly growing. Google Play beats the App Store in terms of numbers, offering users 3.55 million apps and leaving the App Store with 1.95 million behind. That means that the competition in Google Play is much tougher, though.
The app’s position in the market is affected by several factors, and the number of downloads is one of them. Thus, if you want to run a successful app, you need to invest your time, effort, and money not only in the development but also in the App Store Optimization. This should be the foundation of your app marketing strategy.
Learn How to Improve the Visibility of Your App in the Store
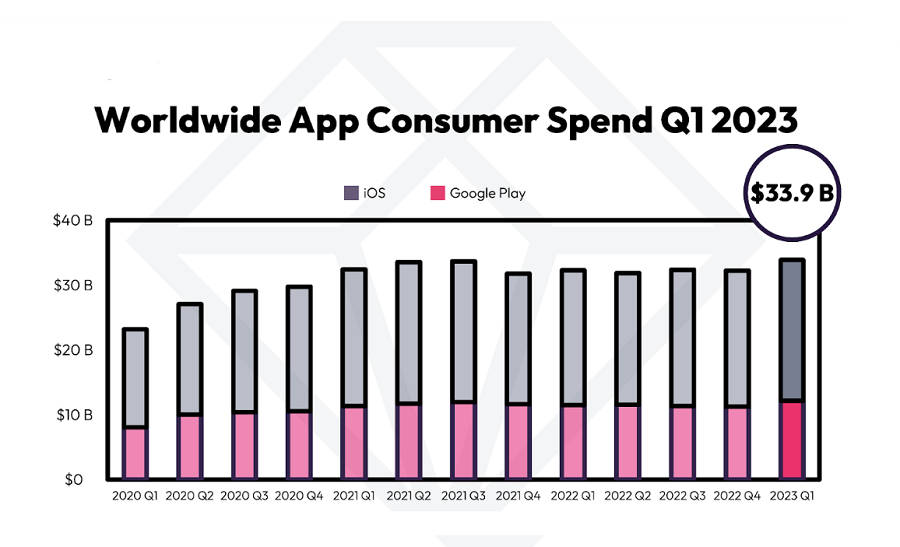
According to data.ai, in Q1 2023, Google Play and App Store app downloads reached 29.1 billion (+1%) and 9.1 billion (+12%) respectively.
At the same time, for Android apps distribution you can use even more than just Google Play. For example, companies can also release their apps on Amazon Store which provides more than 800K apps in 200 countries and enables attracting more users.
As for the revenue share, both stores have similar terms – 30% is taken from in-app purchases in the first year of subscription and 15% of the price after 12 months.
Android Development vs iOS Development
With all the bulk of information mentioned above, it might be easy to lose the thread and get confused. Thus, to provide you with a more structured view of the differences we’ve discussed, here’s a quick recap of the most important moments.
Key Aspects |
iOS |
Android |
|---|---|---|
Global Market Share |
30% | 70% |
Target Audience |
Spend more per app More female users worldwide Preferred by 18-34 age group in US |
Particular prominence in lower-income areas More male users worldwide Preferred by 35+ age groups in US |
Global Customer Spending (2021) |
21.7B | 12.2B |
Number of App Downloads (2021) |
9.1B | 29.1B |
Monetization Strategy |
Focus on Paid Apps In-App Purchases |
Focus on In-App Purchases In-App Adds |
Development Cost |
Less Expensive | Pricier |
Development Timeline |
Faster | Takes More Time |
Development Complexity |
Considered to be easier and faster | Might be more difficult due to tech stack and device fragmentation |
Programming Languages |
Objective-C Swift |
Java Kotlin |
Development Tools |
Apple Code Xcode |
Eclipse Android Studio |
Device Fragmentation |
A few variations of devices | A vast number of devices |
Design Philosophy |
Human Interface Design | Material Design |
Approval Process |
Manual approach Approx 1 week |
Automated tests Less than a week |
Distribution Channels |
App Store | Google Play, alternative app stores, and sideloading |
Distribution Fee |
$99 per year | $25 one-time |
Of course, the list of comparisons can be much longer. Yet, these essential distinctions between iPhone and Android apps development help shape a clear vision and support your decision-making process.
Pros and Cons of Android and iOS App Development
Let’s sum up the upsides and downsides of iOS vs. Android app development so you can make smart choices for your next mobile project.
Android
Android app development offers flexibility and a wide user base, but it comes with device fragmentation challenges.
Pros of Android Development
- Broad user base
- Open-source platform
- Diverse hardware compatibility
- Multiple app distribution channels
- Customization opportunities
- Lower development costs
- Java and Kotlin support
Cons of Android Development
- Security concerns (requires constant updates)
- Varied hardware compatibility due to device fragmentation
- Lower app revenue
- Complex testing process
iOS
iOS app development provides a polished user experience and reliable hardware, but it may involve stricter guidelines and a smaller user base.
Pros of iOS Development
- Polished UI/UX
- Easier compatibility across Apple devices
- Reliable hardware
- Higher revenue potential
- Higher quality standards
- Security features (e.g. advanced biometric authentication)
- Stable ecosystem
- Loyal user base
Cons of iOS Development
- Smaller user base
- Stringent App Store review (causes delayed updates)
- Limited customization
- Closed ecosystem (e.g. limited deep system-level access)
- Costly hardware for testing (requires Apple devices)
Key Takeaways: iOS or Android?
Once again, there are several aspects to take into consideration when choosing the platform for your first app. Your target audience, development budget, timeline, and monetization strategy will definitely impact your decision.
In a nutshell, choose Android if you want to reach a larger market share, be more flexible with customizations, and submit your application to the store faster. However, if your focus is to generate higher revenue per user, target a younger audience, and follow a less intricate development process — opt for iOS.
In our experience, most businesses need help with a decision on what platform to target first. A consultation with a reliable software development vendor could pave the way for your mobile solution. You can simply start with a short discovery meeting and put on the table what you have, even if it’s just an idea or project vision.
Velvetech has vast expertise in mobile app development in both OS. Don’t hesitate to contact us to evaluate your potential app and choose the right platform while avoiding major pitfalls.