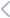In manufacturing, achieving a competitive edge demands efficiency and a grasp of intricate operational data. Here, enterprise manufacturing intelligence is a key player in simplifying complexities and offering actionable insights to the human eye.
Picture a large-scale automotive assembly line where intelligent manufacturing software acts behind the scenes, distilling data from various sources to optimize production flows, identify bottlenecks, and enhance efficiency. Using this approach, a manufacturer will rapidly outperform competitors relying on manual efforts. With this example in mind, embrace the enterprise manufacturing intelligence concept and learn how to apply it in your workflows.
What Is Enterprise Manufacturing Intelligence?
Enterprise Manufacturing Intelligence, or EMI, might sound like a complex term, but at its core, it’s about making sense of manufacturing processes in a smart and efficient way. Simply, EMI is the brain of a manufacturing operation, helping companies derive valuable insights and improve their production processes.
EMI functional focus usually includes:
- Operations
- Strategy and planning
- Quality
- Supply chain
- Energy consumption
- Collaboration
- Regulatory compliance
- Any individual manufacturer needs
The focus areas of EMI reflect the main subject of optimization. Of course, one EMI software can include multiple functions or all listed above. It depends on which components a given EMI software offers.
Learn more about the 16 Essential Software Types for Manufacturers
Key Components of EMI
EMI involves a set of tools and technologies that work together to collect, process, and analyze data from various stages of the manufacturing cycle. It includes things like sensors on machines, software to gather and organize data, and analytics tools to turn that data into useful insights. Thus, EMI has modules to serve every stage from acquiring data to making it readable and accessible for different roles. Let’s take a closer look at all of them.
1. Data Acquisition Systems

EMI relies on robust data acquisition systems to collect real-time data from various sources within the manufacturing environment. These sources include industrial IoT sensors, programmable logic controllers, or PLCs, supervisory control and data acquisition systems, or SCADA, and other instrumentation. The ability to gather data accurately and in real time is crucial for EMI’s effectiveness.
2. Connectivity and Integration Frameworks
EMI also integrates with diverse manufacturing systems, databases, and software applications to support data acquisition and other functions. Connectivity and integration frameworks enable seamless communication between different components of the manufacturing ecosystem. This ensures that data flows cohesively, providing a comprehensive and interconnected view of the entire manufacturing process.
3. Data Historian
Then, the information gathered goes to a data historian, a database specifically designed for collecting, storing, and retrieving time-series data. It plays a vital role in EMI by preserving historical production data. This historical perspective allows for trend analysis, performance comparisons, and the identification of patterns critical for decision-making and process improvement.
4. Visualization and Dashboard Tools

To make the database precious information speak, EMI platforms take advantage of basic business intelligence tools like visualization and dashboards. They help present complex manufacturing data in a user-friendly and comprehensible manner. Graphs, charts, and intuitive interfaces enable operators, managers, and decision-makers to quickly grasp key performance indicators, or KPIs, and make informed decisions.
Read more about How Manufacturers Can Apply Business Intelligence
Defining and monitoring KPIs is a fundamental aspect of EMI. These performance metrics align with the strategic goals of the manufacturing operation and provide a quantifiable measure of success. Common KPIs include OEE, cycle time, yield, and energy consumption.
BI for Business
Find out the secrets of how business intelligence boosts operations and what BI tools and practices drive data analysis.
5. Analytical Engines and Algorithms

When the human eye is no longer able to scrutinize large volumes of information, advanced analytics, and algorithms are employed within EMI to process and analyze these datasets. The engines identify patterns, anomalies, and correlations in the data, providing insights into operational efficiency, quality control, and predictive maintenance. Machine learning algorithms may also be applied for predictive analytics.
6. Reporting and Alerting Mechanisms

Since the main purpose of EMI systems is making a difference with informed decision-making, they incorporate reporting functionalities to generate customizable reports and summaries. Additionally, alerting mechanisms notify stakeholders in real time about deviations, critical events, or performance issues. This proactive approach enables swift responses and minimizes downtime.
Discover How Manufacturers Can Solve Time-Sensitive Issues with IIoT
7. User Role Management and Security Features
Manufacturing intelligence solutions also consider that various departments and employees make those vital decisions. Thus, they implement robust user role management and security features to control access to sensitive manufacturing data. Different stakeholders, from operators on the shop floor to top-level executives, require varying levels of access. Ensuring data integrity and confidentiality is critical in EMI implementations.
8. Mobile and Remote Accessibility

Finally, as the world goes for mobile solutions more often, intelligent manufacturing software is no exception, offering the ability to access EMI data remotely. It usually happens through mobile devices to enhance operational flexibility. Remote accessibility allows stakeholders to monitor and manage manufacturing processes from anywhere, facilitating quick decision-making and responsiveness to changing conditions.
All components eventually contribute to the beneficial effect of tracking and analyzing essential production processes, improving operations, strategy, supply chain, energy consumption, and more.
Benefits of EMI Systems for Production
EMI facilitates real-time monitoring of production lines, machinery, and overall plant performance. For instance, a leading automotive manufacturer can implement EMI solutions to track machine downtime data and optimize production schedules. This is likely to result in improved supply chain and predictive maintenance significantly impacting the bottom line.
In quality control, EMI identifies and addresses defects promptly. A consumer electronics company can use EMI to establish a closed-loop quality control system and reduce product defects within the first year of implementation. This not only bolsters product quality but also fosters customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Take your time to explore how EMI systems optimize other production areas, how they benefit manufacturers, and what software is a good example in its niche.
Functional Focus |
Advantages |
Software Example |
|---|---|---|
| Operations |
|
Aveva |
| Strategy and Planning |
|
SAP Integrated Business Planning, IBM Predictive Maintenance |
| Quality |
|
InfinityQS ProFicient |
| Supply Chain |
|
Oracle SCM Cloud |
| energy consumption |
|
Schneider Electric EcoStruxure |
| Collaboration |
|
Siemens Teamcenter |
| Regulatory Compliance |
|
MasterControl Quality Excellence=sw- |
| Individual Manufacturer Needs |
|
Custom software |
As you can see, the integration of EMI extends beyond the factory floor to encompass the entire supply chain. You can imagine a global pharmaceutical company utilizing EMI to optimize inventory management and demand forecasting. Such improvements underscore EMI’s capacity to create a synchronized and responsive supply chain ecosystem.
EMI’s influence also extends to sustainability initiatives by providing insights into energy consumption patterns. A progressive food processing plant may want to take advantage of EMI to identify energy-intensive processes and implement targeted efficiency measures. This can reduce the facility’s carbon footprint and lead to substantial cost savings, showcasing the dual impact of EMI on environmental stewardship and operational economics.
Explore the Power of Industrial IoT for Achieving Sustainability Goals
Challenges Manufacturers Face in Implementing EMI
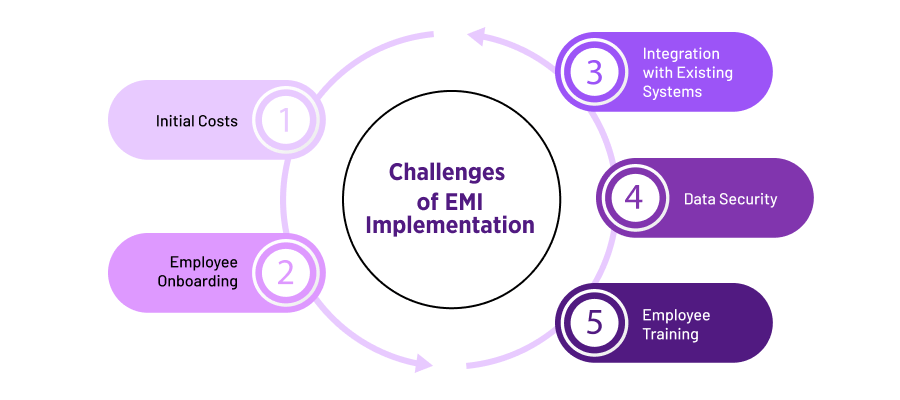
Implementing EMI isn’t always a walk in the park. Setting up an EMI system can be a bit expensive at the start. Companies need to figure out how to manage this initial cost and navigate the complexity of the new system.
Then, employees might not be too excited about new technology. They could worry that it might change their jobs or be challenging to learn. Employers need to help employees feel comfortable and show them how the new system can make things better.
Making the new EMI system work smoothly with the existing systems can also be like fitting puzzle pieces together. Sometimes, it takes a bit of effort to make sure everything connects and works well. Managers should carefully plan how to integrate EMI without causing disruptions.
Keeping all the data safe and secure is another issue. Just like you wouldn’t want your personal information to be exposed, you need to make sure that the information collected by EMI is protected from any unauthorized access.
Finally, learning how to use the new EMI system is a thing to consider for everyone involved. Don’t neglect investing time in training employees so that they feel confident using the system.
Overcoming these challenges requires companies to plan, communicate well with their team, and provide the necessary support. Just like learning anything new, with time and effort, the benefits of EMI can become clear, making the initial challenges worthwhile.
Best Practices for Embracing EMI in Production
Making sure manufacturing intelligence systems work well in your company involves following some smart strategies. Let’s check out the best practices that anticipate some challenges mentioned earlier:
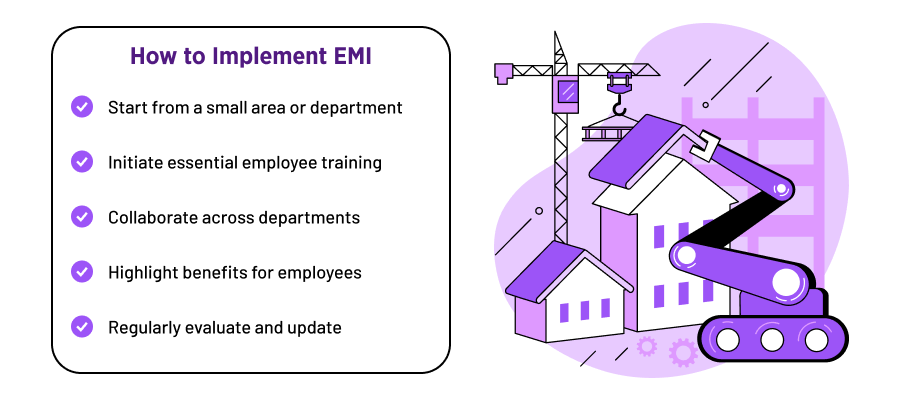
- Start small, grow gradually. It’s like planting seeds in a garden — start with a few and let them grow. Begin by implementing EMI in a small area or department. This way, your team can get used to it without feeling overwhelmed. Once everyone’s comfortable, you can expand it to other parts of the company.
- Training is key. Imagine getting a new gadget -– you need to know how it works to enjoy it fully. The same goes for EMI. Make sure everyone gets the hang of it by providing good training.
- Collaborate across departments. Teamwork makes the dream work. Make sure different departments are working together.
- Highlight benefits for employees. Sometimes, people need to see why something is good for them. Make sure to explain how EMI makes everyone’s job better and contributes to their professional growth. This way, your team is more likely to embrace EMI with open arms.
- Regularly evaluate and update. Imagine having the latest version of your favorite app with new features. EMI is similar — keep it fresh and updated. Regularly check how well it’s working and if there are new things it can do. This way, it stays helpful and aligned with what your company needs.
With a bit of planning and teamwork, implementing EMI becomes smoother and more successful for your company. Even more, following the regular update advice, you will be always well-prepared for future developments.
The Future of EMI
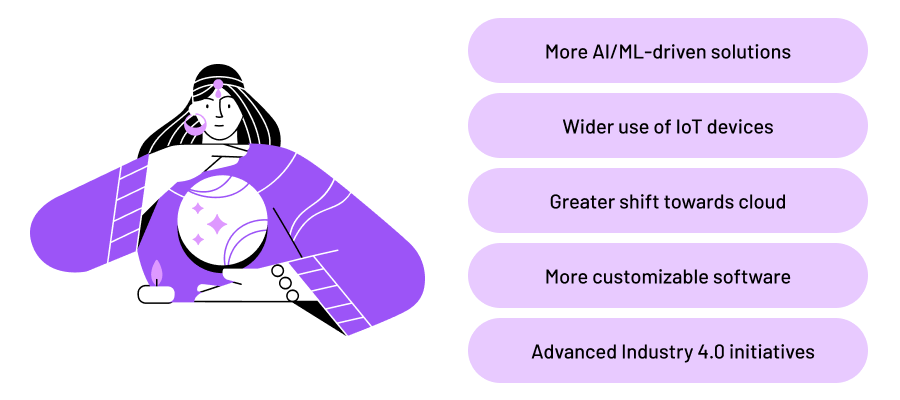
Looking ahead, the future of EMI is set to become increasingly sophisticated with the rapid progress of technology. Popular tools like artificial intelligence and machine learning are poised to take on more prominent roles, bringing enhanced capabilities to manufacturing.
For instance, when faced with unexpected changes in demand or supply chain disruptions, the AI within EMI can dynamically adjust production schedules, predict maintenance needs, and fine-tune operational parameters.
Moreover, the integration of IoT devices into manufacturing processes will usher in a new era of intelligent and adaptive systems. The synergy of these advancements promises to shape a future where EMI not only simplifies but positively changes how manufacturing operations are monitored, analyzed, and optimized.
Expect a greater shift towards cloud-based EMI solutions. This transition will offer advantages like increased scalability, accessibility, and collaboration across diverse manufacturing locations. Cloud-based EMI will streamline data storage, processing, and accessibility for improved efficiency.
EMI systems will become more customizable to suit the unique needs of different industries and manufacturing processes. Tailored custom software solutions will allow companies to implement EMI in a way that aligns precisely with their specific challenges and goals.
EMI will align closely with Industry 4.0 initiatives, too, contributing to the broader vision of smart, connected factories. The integration of EMI with other Industry 4.0 technologies like robotics, digital twins, and augmented reality will create a synergistic approach to modernizing manufacturing operations.
Time to Fuel Production with Data-Driven Intelligence
So, enterprise manufacturing intelligence software empowers companies to improve their production processes, enhance product quality, and stay competitive. While there are challenges in implementing EMI, the benefits far outweigh them. By embracing best practices and keeping an eye on trends, companies can unlock the full potential of EMI and pave the way for a more efficient and successful manufacturing journey.
The future of manufacturing software promises to be dynamic, driven by a convergence of advanced technologies. It is predicted to simplify and transform manufacturing intelligence, ushering in an era of unprecedented efficiency, adaptability, and innovation in the manufacturing sector. Reach out to us and make sure you stay among the first manufacturers to adopt the data-driven today and tomorrow!