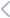Welcome to the era of Industry 4.0, where technology and innovation are taking manufacturing to a new level. Beyond smart manufacturing and industrial automation, Industry 4.0 extends its transformative influence across diverse sectors. From construction to logistics, its pervasive impact reshapes operations and establishes a new echelon of efficiency and connectivity.
What Is Industry 4.0
The evolution of Industry 4.0 traces back to the early 21st century, marked by the convergence of digital solutions with traditional industrial processes. Initially coined in Germany, this Fourth Industrial Revolution has progressively matured, influencing diverse sectors globally.
At its core, Industry 4.0 is a comprehensive framework that combines the newest technologies to upgrade industrial processes and production. These technologies include:
- Internet of Things
- Cloud computing
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Edge computing
- Cybersecurity
- Augmented reality and virtual reality
- Digital twins
- Additive manufacturing
- Robotics
Industry 4.0 represents the amalgamation of these smart manufacturing technologies, creating a holistic and interconnected ecosystem where machines, systems, and humans collaborate seamlessly. This integration fosters a highly adaptable and intelligent industrial environment.
Learn more about How to Simplify the Complex with Manufacturing Intelligence
Industry 4.0 Examples Across Industries
Various industries are embracing cutting-edge technologies proclaimed by Industry 4.0 to make the most of production and other processes. Let’s look at how Industry 4.0 use cases are making a positive impact in the manufacturing sector first.
1. Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, Industry 4.0 is ushering in a new era of smart factories and connected processes. Audi, a leading automobile manufacturer, collects and analyzes volumes of data from various sources within the production line to gain insights into efficiency, quality, and resource utilization.
The data-driven approach allows for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime, and making sure that machinery operates at peak performance. Ultimately, big data and business intelligence in manufacturing are helping companies like Audi elevate productivity and create high-quality goods and vehicles.
Warehouse management also gets smarter in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Automated systems, including robotics and smart inventory tracking, are streamlining the movement of goods within warehouses. They accelerate order fulfillment and minimize errors to reduce operational costs. By implementing the newest technologies in warehouse management, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of accuracy and responsiveness in their supply chain processes.
Discover How Mobile Technologies Transform Warehouses
2. Logistics
Industry 4.0 is reshaping the way companies manage their supply chains. Technologies like artificial intelligence and data analytics, optimize the entire logistics process. From inventory management to order fulfillment, companies are using smart systems to refine operations, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency.
Besides, Industry 4.0 is empowering businesses to proactively identify and manage risks in the supply chains. Through the integration of real-time data and predictive analytics, companies can assess potential disruptions and develop contingency plans. This creates a more resilient supply chain that adapts swiftly to unforeseen challenges and minimizes the impact of disruptions on operations.
Learn about Capitalizing on Data Analytics in Supply Chain Operations
IoT is key in optimizing transportation within Industry 4.0. Again, smart sensors and connected devices are being embedded in vehicles, containers, and infrastructure to collect and share data quickly. Thus, companies can track shipments, improve routes, and monitor the condition of goods during transit.
One tangible example of Industry 4.0 in transportation is Volvo’s tracking system. Utilizing advanced telematics and GPS technology, Volvo allows companies to monitor the location and status of their vehicles. It enhances fleet management and enables businesses to make informed decisions, improve fuel efficiency, and provide better customer service through accurate delivery predictions.
Our collaboration with Cargo Data has also yielded innovative technologies for cold chain monitoring in logistics. It included the development of iMAT firmware terminals and Lightning NFC, a technology for efficient temperature tracking. The GPS monitoring system offers real-time insights into truck location and temperature data.
Now, the deployment of devices in 10-12k trucks happens monthly, resulting in faster project turnarounds and cost savings. Cargo Data, equipped with patented cold chain monitoring solutions, remains at the forefront of the industry.
Learn more about how we implemented IoT for Cold Chain Monitoring
3. Retail & E-commerce

Industry 4.0 is bringing about significant changes to the retail and e-commerce services. It is putting a spotlight on personalized shopping experiences and goods production.
Retailers and e-commerce platforms are leveraging data analytics and machine learning algorithms to understand customer preferences and behaviors. They analyze purchase history, browsing patterns, and other relevant data to offer personalized designs, targeted promotions, and customized content.
Efficient stock management is crucial in retail, too, and Industry 4.0 technologies are here to assist businesses in inventory handling. Automated stock tracking systems utilizing RFID technology and IoT sensors provide real-time visibility into stock levels, helping retailers maintain optimal inventory levels, avoid stockouts, and minimize overstock situations.
Explore How IoT Boosts Retailer’s Competitiveness
4. Construction
In the construction field, Industry 4.0 is driving transformation, productivity, and sustainability. One of the notable applications is the use of digital twins. This technology creates virtual replicas of physical structures for monitoring and analysis.
Construction companies can use digital twins to simulate and optimize building processes, detect potential issues, and improve project management. The technology secures accuracy in construction planning, eliminates errors, and contributes to the success of construction projects.
Industry 4.0 is also optimizing site management through the integration of other intelligent technologies. Dinamic Oil, for example, gained a substantial competitive advantage with a smart IIoT system for construction that is rare in this niche. The system enhanced the functionality of the company’s gear products, improving sales opportunities. Torque and speed sensors, coupled with mobile and desktop apps, provided transparency and control over helical pile installation, facilitating the monitoring of crucial data.
Read the full case on IIoT System Development for Engineering
Last but not least, Building Information Modeling, or BIM is a key component of Industry 4.0 in construction. BIM involves creating detailed digital representations of a building’s physical and functional characteristics. This technology facilitates collaboration among different stakeholders, including architects, engineers, and contractors.
Through BIM, construction professionals visualize the entire lifecycle of a construction project, from design and actual construction to operation and maintenance. The application of BIM results in better coordination, reduced rework, and better project outcomes.
5. Agriculture
Surprisingly or not, Industry 4.0 is changing the way we grow, process, and distribute food. It is the engine behind precision agriculture. Farmers use technologies such as cloud, IoT apps, drones, and sensors to monitor and manage crop conditions. The data-driven practices enable more precise irrigation, fertilization, and pest control to increase crop yields, optimize resource usage, and encourage sustainability in food production and plant nurturing.
A plant-growing company, Leider Greenhouses successfully took advantage of smart technologies to achieve its long-term goal. It involved migrating its legacy plant-growing algorithms, rooted in centuries of experience, into a modern cloud application. This new app operates faster and is accessible from anywhere, providing enhanced flexibility compared to the original desktop applications confined to office workstations.
The comprehensive update of their infrastructure fosters seamless operations. These changes have resulted in a lower cost of plant production, making the workforce more productive. The viable production system, securely deployed on the client’s servers, keeps data protected without any risk of loss or breach.
Read more on how a Plant-Growing Company Benefitted from Legacy Software Migration
6. Fieldwork

In various fields, from environmental research to telecom and energy, Industry 4.0 is bringing about new ways of how fieldwork is conducted. Like other professionals from the article, fieldworkers benefit from Industry 4.0 through the use of IoT sensors. They help with inventory management and data collection on various parameters, such as air and water quality, biodiversity, and climate conditions.
The data generated by IIoT sensors allows scientists to monitor ecosystems more comprehensively, analyze trends, and make informed decisions for conservation and sustainable resource management.
Find out How to Reach Sustainable Goals with IoT
Another way Industry 4.0 is enhancing field inspections is through the integration of AR tools. Fieldworkers can use AR-equipped devices to overlay digital information onto their physical surroundings. This aids in tasks such as equipment inspections, maintenance, and repairs. AR-guided instructions provide fieldworkers with relevant information to decrease the likelihood of errors in complex fieldwork scenarios.
7. Product Design

Smart manufacturing concepts for product design and realization are possible through the integration of robotics and automation. Robotic systems help in tasks such as precision cutting, assembling, and finishing.
Digital design technologies discussed earlier also empower product manufacturers to offer customizable items at scale. Here, Industry 4.0 encourages the implementation of Computer-Aided Design, or CAD and 3D modeling so that designers can create intricate and personalized pieces.
Virtual reality and augmented reality enter the design phase to help engineers and designers visualize and test products in a virtual environment before physical prototypes go live. The approach accelerates the product development cycle, reduces spending associated with physical prototyping, and enables iterative design improvements.
Even more, advanced technologies help explore and implement eco-friendly materials and production methods. Then, data analytics step in to optimize resource usage, cut down waste, and track the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. The commitment to sustainability aligns with the growing demand for eco-conscious products across industries.
8. Healthcare
In healthcare, Industry 4.0 tech primarily improves supply management. Smart sensors and data analytics help hospitals and clinics keep track of their inventory in real time. This means that essential medical supplies and medications can be monitored, ordered, and restocked timely. Thus, healthcare providers have what they need when they need it.
Read about how we developed a Real-Time Location Tracking System for a Healthcare Company
ndustry 4.0 is bringing a personalized touch to patient care, too. Electronic Health Records, or EHR, and connected devices allow healthcare professionals to access comprehensive patient information instantly. This fosters communication among healthcare teams and makes it easier to design more coordinated and personalized patient treatment plans.
Overall, with the help of Industry 4.0 technologies, healthcare is becoming increasingly personalized. Advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms analyze patient data to predict and prevent diseases. Healthcare providers are now also capable of linking treatment plans based on individual patient needs in pursuit of better healthcare outcomes.
Explore How Urology Specialists Use Software for Remote Patient Monitoring
9. Public Transportation
Finally, Industry 4.0 is driving innovation to positively impact the passenger experience. Intelligent sensors and IoT devices are integrated into buses, trains, and other vehicles to provide data on their status, location, and performance. Thus, transportation software helps create better routes and schedule maintenance proactively. Passengers, in turn, benefit from improved reliability and timely services.
Digital ticketing solutions, mobile apps, and contactless payment methods are becoming increasingly prevalent, too. These technologies simplify the passenger experience and reduce queuing times. Besides, data analytics from these systems provide valuable insights for transportation authorities to make better fare structures and service planning.
As for maintenance, the predictive powers of Industry 4.0 come in incredibly handy. Sensors and data analytics monitor the condition of vehicles and infrastructure to predict potential issues before they lead to breakdowns. By using this technology, companies minimize downtime, ensure the reliability of transportation services, and contribute to cost savings for transit agencies.
Become a Part of the 4th Industrial Revolution
As you’ve seen in our exploration of Industry 4.0 examples across various sectors, the transformation is tangible and far-reaching. From retail’s personalized touch to logistics optimization, manufacturing’s smart processes and construction’s innovation, Industry 4.0 has impacted it all.
Join the 4th industrial revolution by incorporating Industry 4.0 trends and technologies into your business. Whether you’re looking to optimize processes, enhance customer experiences, or streamline operations, our expert industrial automation services are here to guide you. Let’s collaborate to shape a future where innovation and efficiency go hand in hand.